Drone Mapping with LiDAR and Photogrammetry
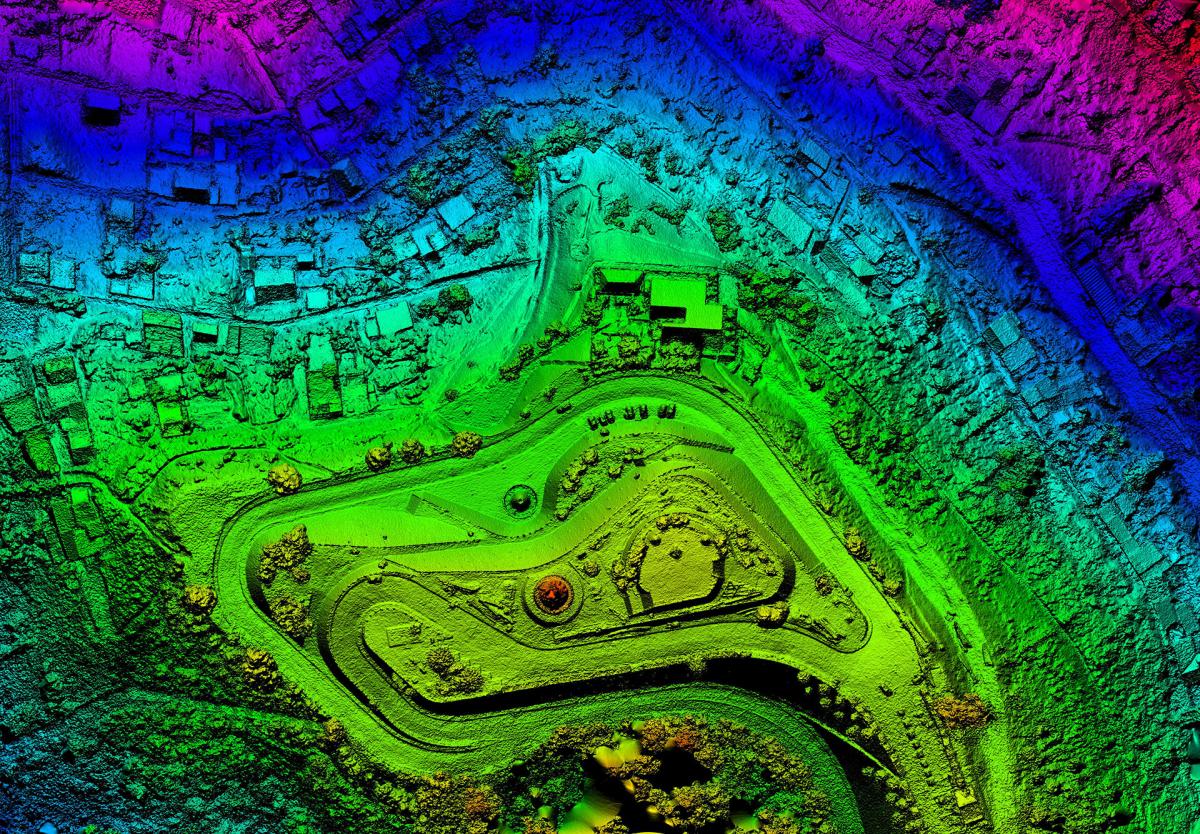
Scan Skunks is proud to offer drone LiDAR and Photogrammetry services. Not until the last 3-4 years has drone photogrammetry begun to take over as an acceptable form of measurement for the built form. Scan Skunks has and maintains Part 107 license to operate for commercial purposes. We are also insured to fly. When it comes to scanning large acreages, capturing topographical data, creating as-builts, and penetrating tree canopies, Scan Skunks' drone LiDAR scanning offers unparalleled advantages. Our cutting-edge technology empowers developers, and environmental planners with accurate, actionable data, even in challenging terrains. Here’s how our drone LiDAR services stand out.
High-Precision Acreage Scanning
For large parcels of land, traditional surveying methods can be time-intensive and laborious. Scan Skunks’ drone LiDAR technology simplifies this process, capturing vast acreages in a fraction of the time without compromising accuracy. By flying drones over large areas, we gather high-resolution data that covers every inch of the property. This data allows stakeholders to make well-informed decisions, whether for real estate development, environmental studies, or land management.
Detailed Topographical Mapping
Topography plays a crucial role in any development project, as it directly affects site planning, water drainage, and grading. Using drone-mounted LiDAR, Scan Skunks provides comprehensive topographical maps that reveal elevation changes, slope variations, and other terrain features. Our detailed mapping supports engineers and architects in creating designs that work with the land’s natural characteristics, improving sustainability and reducing costly modifications during construction.
Accurate As-Builts for Project Verification
In the realm of civil engineering, as-builts are essential for confirming that projects align with design specifications. Scan Skunks specializes in using drone LiDAR scanning to produce accurate as-builts, ensuring that what exists on the ground matches the project’s plans. By providing these precise, current as-builts, our technology streamlines inspections, improves quality control, and supports regulatory compliance, all while reducing the need for multiple site visits.
Canopy Penetration for Forested and Vegetated Areas
A unique advantage of LiDAR scanning technology is its ability to “see” through tree canopies and dense vegetation, capturing the land surface beneath. This feature is invaluable for environmental assessments, forestry management, and any project in densely vegetated areas where traditional surveying falls short. With our drone LiDAR’s canopy-penetrating capabilities, Scan Skunks captures the full scope of the terrain, from ground level to tree height, providing a complete picture for planners and environmental scientists.
Why Choose Scan Skunks for Drone LiDAR Scanning?
- Fast and Efficient Data Collection: Cover large areas quickly, reducing time on-site and accelerating project timelines.
- High-Resolution, Accurate Data: Our state-of-the-art LiDAR equipment delivers precision measurements, essential for projects requiring exact dimensions and contours.
- Cost-Effective: By using drones, we make it economical to scan areas that are difficult to get to by foot.
- Detailed Analysis and Reporting: Our team provides detailed reports and data sets tailored to your project’s unique requirements, from raw point clouds to refined digital terrain models.
Applications Across Multiple Industries
Drone LiDAR scanning has broad applications, from infrastructure development to environmental conservation and real estate. Developers gain insights into land usability, civil engineers can streamline project verification, and environmentalists can monitor ecosystem health — all thanks to the versatility of Scan Skunks’ drone LiDAR solutions.
Scan Skunks' drone LiDAR scanning services deliver top-quality, efficient, and precise land analysis. Whether you need to scan acreage, capture topography, verify as-builts, or scan through dense tree cover, our advanced technology and expertise ensure that you receive the data needed to make informed decisions. Choose Scan Skunks to unlock the full potential of your land with reliable, high-resolution data and exceptional service.
Photogrammetry
Drone photogrammetry is a technique that uses unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), to capture high-resolution photographs of an area or object from multiple angles and then process these images to create detailed 3D models, maps, and measurements. This technology combines principles of photography, remote sensing, and computer vision to extract valuable spatial information from the collected imagery. Here's a breakdown of the key components and steps involved in drone photogrammetry:
-
Data Collection:
- A drone equipped with a camera is flown over the area of interest.
- The camera captures a series of overlapping images from different angles, typically in a grid or along defined flight paths.
- Ground control points (GCPs) with known coordinates are placed in the survey area. These GCPs serve as reference points for accurate georeferencing.
-
Image Processing:
- The captured images are transferred to a computer for processing.
- Software tools, often specialized photogrammetry software, are used to analyze the images.
- The software identifies common features or points in the overlapping images (keypoints) and calculates the relative positions and orientations of the images. This process is known as "image matching."
-
Creating a Point Cloud:
- Once the images are aligned, the software generates a dense point cloud. This point cloud is a 3D representation of the surveyed area, with each point having X, Y, and Z coordinates.
-
Surface Reconstruction:
- The point cloud can be used to create a 3D mesh or surface model, which represents the terrain or object's external shape.
-
Texture Mapping:
- The high-resolution images are then draped or projected onto the 3D model's surface to add realistic textures and colors.
-
Data Analysis and Visualization:
- The resulting 3D models, maps, and orthophotos (geometrically corrected aerial images) can be used for various applications:
- Topographic Mapping: Creating accurate elevation models and contour maps for land surveying and terrain analysis.
- Agriculture: Monitoring crop health, estimating yield, and managing land.
- Construction: Tracking progress, conducting site inspections, and planning.
- Environmental Assessment: Monitoring natural resources, ecosystems, and habitats.
- Archaeology: Documenting and preserving archaeological sites.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Inspecting bridges, buildings, and other structures for maintenance or damage assessment.
- Disaster Response: Assessing damage after natural disasters and planning recovery efforts.
- The resulting 3D models, maps, and orthophotos (geometrically corrected aerial images) can be used for various applications:
-
Data Sharing and Integration:
- The generated data can be easily shared with stakeholders, integrated into GIS (Geographic Information Systems) platforms, and used for decision-making and analysis.
Drone photogrammetry offers several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and the ability to collect highly detailed and up-to-date spatial information. It has revolutionized various industries by providing a valuable tool for mapping, monitoring, and analyzing geographical and environmental data.
Disclaimer: Scan Skunks are not licensed surveyors. The data collected from our Lidar and mapping devices is not to be used for authoritative surveying purposes. We do not provide boundaries, ALTA surveys, or floodplan mapping.
